![]()
A satellite in equatorial orbit flies along the line of the Earth's equator. To get into equatorial orbit, a satellite must be launched from a place on Earth close to the equator. NASA often launches satellites aboard an Ariane rocket into equatorial orbit from French Guyana.
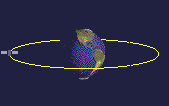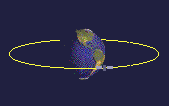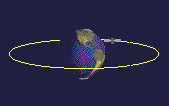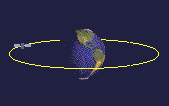
Equatorial orbits can be useful for satellites observing tropical weather patterns, as they can monitor cloud conditions around the globe.
Equatorial orbits are usually medium or low orbits.